What is Energy Recovery Ventilator or What is ERV?
Homes and buildings are being made or restored to be closer than ever before to retain energy. Sealing slots and cracks in the building envelopment ceases the reciprocity of air with the outside, preserving energy and promoting solace. ERV stands for Energy Recovery Ventilator, with ordinary name variations containing ERV air exchangers and ERV ventilation systems. An ERV presents a method of transferring new, temperature-controlled air into the house while taking out musty, poisonous air. ERVs are systems designed to be joint to the channels that are sections of the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. Using two fans, ERVs pull neat and new air into a home or office and take stale air away. An ERV permits fresh air to a building while keeping preconditioned heating or cooling.
This kind of device also catches some of the moisture in the air to retain it on the identical side of the thermal cover that it came from. If the house is excessively dry in winter, an ERV would be the most effective option as it helps keep humidity, removing the need and cost to produce it within other means (for more information, click here). Along with this transition of airflows, ERV ventilation systems catch pollutants, allergens, pollen, contaminants, and more, ensuring that the air that arrives and is kept inside the home or office is healthy and clean.
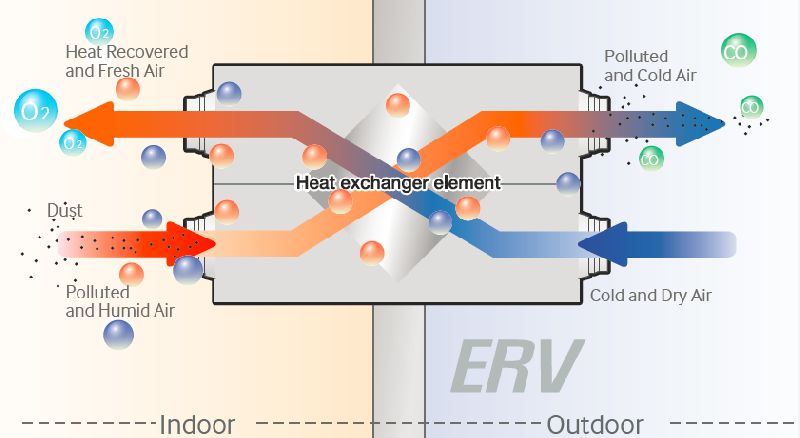
How it Works
Although some window or wall-mounted units are available, HRVs and ERVs are most often designed to be placed in the ducts of a whole-house heating and cooling system. The heat exchanger is the heart of an HRV, usually consisting of a box-shaped transfer unit made from special conductive materials. Incoming and outgoing air streams pass through different sides of the box (but are not mixed), allowing conditioned exhaust air to raise or lower the temperature of incoming fresh air. ERVs also allow the exchange of moisture to control humidity. This can be especially valuable in situations where problems may be created by extreme differences in indoor and outdoor moisture levels. For instance, in cold climates better air flow and additional humidity inside can help control window condensation. In humid summer climates, it can be critical to dry out incoming air so that mildew and mold do not develop in ductwork.
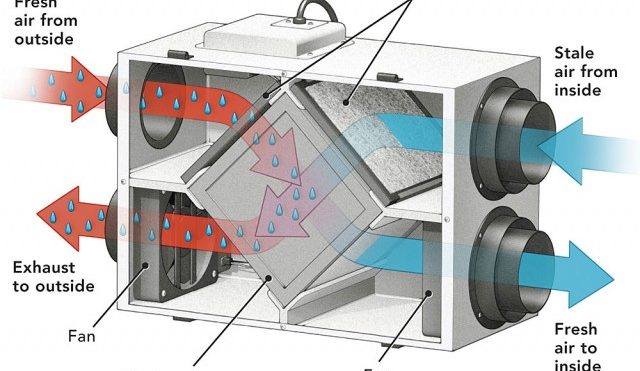
After passing through the heat exchanger, the warmed or cooled fresh air goes through the HVAC air handler, or may be sent directly to various rooms. Stale air from return ducts warms or cools the incoming air, depending on the season, before being exhausted outdoors.
Conventional fan and vent units, often required by code in baths and kitchens, may allow significant energy losses. An HRV system can incorporate small, separately switched booster fans in these rooms to control moisture or heat generated by activities like showering or cooking. Odors and pollutants can be quickly removed, but energy used to condition the air is recycled in the heat exchanger. Some codes or applications may still require stoves to be separately vented for removal of grease or gas fumes.
Energy Recovery Ventilator’s internal parts
- A wheel is a plastic or metal implement that spins between the exhaust and outdoor air flows. It raises heat from one airflow and transmits it to the other. Wheels are the most admired ERV because of their comparatively low primary cost, the facility of maintenance, sensible pressure drop, and smaller physical footprint.
- Heat pipes are somewhat restricted because they cannot revive hidden energy. They are practical-only energy- restoration systems. Heat pipes are tubes from copper with refrigerant inside them. These tubes operate between the two airflows (outside and exhaust air). One airflow heats the refrigerant inside the tube, making it to vaporize. That refrigerant vapor then transfers down the pipe to the other airflow. When the other airflow chills the pipe, the refrigerant condenses, warming the cooler air stream in the procedure.
- Fixed-core plates normally are greater in size and more expensive than wheels but have no rotating sections and can be utilized in specified usages (such as hospitals) where a wheel may not be allowed. As an alternative of a wheel rotating between air flows to shifts energy, the air streams move by each other within a series of ducts, cooling down or heating up the substance among the channels and conveying energy. Fixed-core plates can be plastic, metal, or even paper.
- Runaround coils assign some homogeneous with heat tubes but often are selected when the exhaust and outdoor air streams are detached by large spaces. This kind of system needs installing a water coil in the external airflow and a second one in the entering outdoor/ventilation airflow. Like heat pipes, these systems only are able to move practical energy, not latent energy.
Energy Recovery Ventilator Cost
Energy recovery ventilators save on energy costs by preserving energy and decreasing the amount of energy needed to cool or heat new air brought inside the home. ERVs, the developed type of an air exchanger, conserve energy by retrieving some of the energy before it goes out of the house. The national mean for an energy recovery ventilator in the United States with its installation is approximately $2,000. This number ranges by the area according to the cost of labor and the brand selected.
Adding an ERV is an ideal method to meliorate the performance of the HVAC system. It could be low-cost repair if the goal is to reduce the costs to operate the system. This system needs little maintenance and preservation. The ERVs’ filters should be replaced or cleaned quarterly, or every 90 to 120 days. A Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV), for the ERVs’ filters, generally costs between $7.00 – $20.00.
The ERV cost is much less when combined with the costs of the regular maintenance, repairs, and installation of the HVAC system or a new furnace. This is because installing a new channel for an ERV is much easier while the basic ducting for the furnace is previously taken apart, the technician is already working, their main equipment is already existing, and the worksite is organized. Finally, on the subject of ROI, the mediocre time to regain the finance through decreased energy costs is three months to three years according to energy consumption. These systems save the homeowner money on usefulness bills. Also, some regions propose considerable discounts and rebates for installing energy-efficient home instruments.
Related Products Panasonic ERVs

JK HVAC We install, repair and service all brands of air conditioners! Including air conditioner cleaning, dryer vent cleaning, furnace repair.
📍 Serving all of New York City: Manhattan, Brooklyn, Staten Island, Queens…





